Soccer and Newton’s First Law of Motion might seem unrelated. But they share an interesting connection.
Newton’s First Law states that an object remains at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by a force. In soccer, the ball stays still until kicked, or it continues moving until stopped by a player or obstacle. The law explains much of the game’s dynamics.
Players use force to pass, shoot, and tackle. Understanding this law helps players improve their game. It makes their actions on the field more effective. In this blog, we’ll explore how soccer illustrates Newton’s First Law. This will give you a new perspective on the sport and its physical principles.
Introduction To Soccer And Newton’s First Law
Soccer is a beloved sport around the world. It is a game of strategy, skill, and teamwork. But did you know that soccer also relates to science? Specifically, Newton’s First Law of Motion. This law explains how objects move and react to forces. In this blog post, we will explore the connection between soccer and Newton’s First Law.
Basic Principles Of Soccer
Soccer is played on a rectangular field. Each team has 11 players, including a goalkeeper. The goal is to score by getting the ball into the opposing team’s net. Players use their feet, head, and body to control the ball. The game is fast-paced and requires quick thinking and agility.
- Dribbling – Moving the ball with short touches.
- Passing – Sending the ball to a teammate.
- Shooting – Kicking the ball towards the goal.
- Tackling – Attempting to take the ball from an opponent.
These basic principles of soccer are essential. They help players control the game and work together as a team.
Newton’s First Law Explained
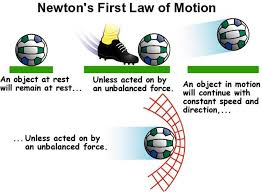
Newton’s First Law of Motion states: “An object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion, unless acted upon by an external force.” This means that an object will not change its state unless a force is applied to it.
Consider a soccer ball on the field. If it is not moving, it will stay still until a player kicks it. This kick is the external force. Once the ball is moving, it will keep moving in a straight line. It will not stop unless another force acts on it. This could be a player stopping it, the ball hitting a goalpost, or friction from the grass.
Here is a simple table to illustrate:
| State | Without Force | With Force |
|---|---|---|
| At Rest | Stays at Rest | Begins to Move |
| In Motion | Continues in Motion | Changes Direction or Stops |
This law is always in play during a soccer game. Every pass, shot, and tackle involves forces changing the motion of the ball.
“`Inertia In Soccer
Understanding how soccer relates to Newton’s First Law of Motion can be fascinating. This law, often called the Law of Inertia, states that an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an external force. Soccer provides clear examples of inertia in action. Let’s dive deeper into the concept of inertia and see how it appears in soccer.
Concept Of Inertia
Inertia is an object’s resistance to any change in its state of motion. If an object is at rest, it resists movement. If it is moving, it resists changes to its speed or direction. This resistance is due to the object’s mass. The greater the mass, the greater the inertia. In soccer, the ball and players exhibit inertia.
Examples Of Inertia In Soccer
Consider a soccer ball at rest on the field. It stays still until a player kicks it. The kick acts as an external force, overcoming the ball’s inertia. Once in motion, the ball keeps moving in a straight line at a constant speed. It will continue until friction with the ground or another force, like a player, stops it.
Another example is a player running with the ball. The player wants to change direction quickly to evade an opponent. The player’s mass and speed create inertia, making it harder to change direction instantly. The player needs to apply force to overcome this inertia.
Goalkeepers also deal with inertia. A goalkeeper standing still must react quickly to an incoming shot. Their body resists the sudden movement, showing inertia at work.
Ball Movement And Newton’s First Law
Soccer is a thrilling sport that demonstrates many scientific principles. One key principle is Newton’s First Law of Motion. This law states that an object will stay at rest or keep moving unless acted upon by an external force. Let’s explore how this law applies to the movement of the soccer ball.
Initial Motion Of The Ball
The ball at rest on the soccer field shows Newton’s First Law. It stays still until a player kicks it. The kick acts as an external force that sets the ball in motion.
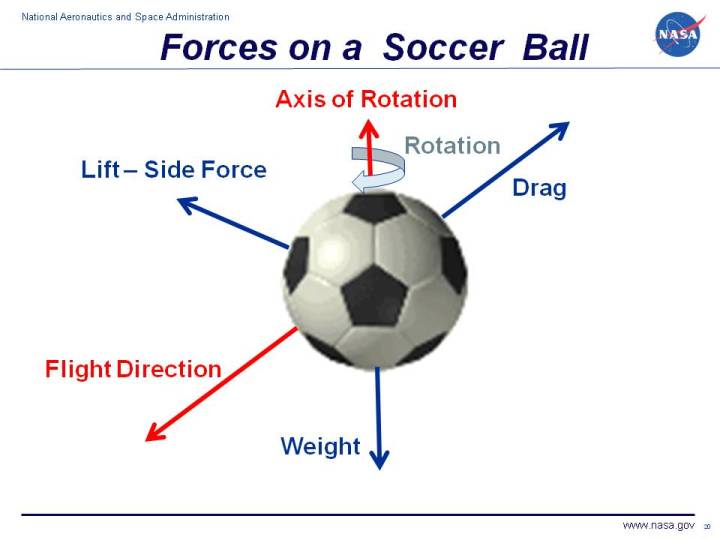
Once the ball is kicked, it moves in the direction of the force applied. The ball continues moving until another force acts on it. This could be friction from the grass, air resistance, or another player’s kick.
Forces Acting On The Ball
Several forces act on the ball during a soccer match:
- Kicking Force: The player’s foot applies force to start the ball’s motion.
- Gravity: This force pulls the ball towards the ground.
- Friction: The grass creates friction, slowing the ball down.
- Air Resistance: Air pushes against the moving ball, affecting its speed and direction.
These forces cause the ball to change speed and direction. Without these forces, the ball would continue moving indefinitely once kicked.
To sum up, Newton’s First Law of Motion is evident in soccer. The ball’s motion, influenced by various forces, highlights the principles of physics in sports.
Credit: schooltutoring.com
Player Movement On The Field
Soccer players are in constant motion during a match. Their movements align with Newton’s First Law of Motion. This law states that an object in motion stays in motion, and an object at rest stays at rest, unless acted upon by an external force. Let’s explore how this law plays out on the soccer field.
Starting And Stopping
A soccer player remains still until they decide to move. The decision to run, kick, or change direction involves applying force. Once in motion, a player continues moving in a straight line at a constant speed. This happens until another force, such as friction or a tackle, causes them to stop or change direction.
Consider a player sprinting towards the goal. They keep moving forward due to their momentum. But, if a defender blocks their path, the player must stop or alter course. This interaction highlights Newton’s First Law in action.
Impact Of External Forces
External forces significantly affect player movements. These forces include friction, gravity, and physical contact from other players. For instance, the friction between a player’s shoes and the field allows them to run and stop effectively. Without sufficient friction, players would slip and struggle to control their movements.
Gravity also plays a crucial role. It keeps players grounded, enabling them to push off the ground and move. Additionally, physical contact from other players, like tackles, can abruptly change a player’s motion. These forces demonstrate how external factors influence movement on the field, adhering to Newton’s First Law.
Understanding these principles helps players improve their game. By recognizing how forces affect movement, players can enhance their strategies and performance.
Friction And Its Role
Friction plays a key role in soccer. It affects the movement of the ball and players. Understanding friction can help improve gameplay. This section will explore how friction influences soccer.
Types Of Friction In Soccer
There are two main types of friction in soccer: static friction and kinetic friction.
- Static Friction: This occurs when the ball is at rest. It keeps the ball from moving until a player kicks it.
- Kinetic Friction: This happens when the ball is in motion. It slows the ball down as it rolls across the field.
Effects Of Friction On Ball And Players
Friction affects both the ball and the players in different ways.
| Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Ball |
|
| Players |
|
Understanding these types of friction can help players make better decisions on the field. By considering friction, players can improve their control and movement, leading to a more effective game.
Impact Of Air Resistance
Soccer is not just about kicking the ball. Physics plays a big role. One key factor is air resistance. It affects how the ball moves. Newton’s First Law of Motion states that an object will stay still or keep moving unless acted upon by an external force. Air resistance is one such force. Let’s explore its impact on soccer.
How Air Resistance Affects The Ball
When a soccer ball is kicked, it moves through the air. The air pushes against the ball. This is air resistance. It slows down the ball. The ball would keep moving forever if there were no air resistance. But air resistance makes it stop.
Air resistance depends on the ball’s speed and surface. A fast-moving ball faces more resistance. A rough ball faces more resistance too. The ball’s path can also change due to air resistance. It can make the ball curve or dip.
Here is a table showing the factors affecting air resistance:
| Factor | Effect on Air Resistance |
|---|---|
| Speed | Higher speed increases resistance |
| Surface | Rough surface increases resistance |
Adjustments Made By Players
Players adjust their play due to air resistance. They kick the ball harder to counteract it. They aim higher or lower to adjust for the curve. Here are some strategies:
- Kicking Harder: Players kick the ball with more force. This helps the ball travel further.
- Adjusting Aim: Players aim higher or lower. This helps manage the ball’s curve.
- Ball Spin: Adding spin to the ball. This can help control its movement.
Players practice these techniques. They learn how to deal with air resistance. It becomes a natural part of their game.
Practical Examples In Matches
Understanding how Newton’s First Law of Motion applies to soccer can change the way we watch the game. In every match, this law is in action. Let’s explore some practical examples seen on the field.
Real-life Scenarios
Consider a soccer ball at rest. It will stay still until a player kicks it. This is Newton’s First Law in action. The ball moves only because an external force acts on it. During a match, players constantly apply forces to the ball, causing it to move.
Now think about a player running with the ball. The player keeps moving in a straight line until they decide to stop or turn. This is because of inertia. The player’s body wants to keep moving in the same direction. To change direction, the player applies a force with their feet to the ground.
Another scenario is a goalkeeper catching a ball. The ball travels in a straight line towards the goalkeeper. It would keep moving in that direction if not for the goalkeeper’s hands stopping it. This again shows Newton’s First Law. The ball’s motion changes only when an external force acts on it.
Analysis Of Famous Plays
Let’s look at some famous plays in soccer history. In the 2014 World Cup, James Rodriguez scored a stunning goal against Uruguay. As the ball flew through the air, it followed a straight path. Rodriguez’s powerful kick applied an external force, setting the ball in motion. The ball’s motion was only stopped by the net.
Another example is Lionel Messi’s dribbling skills. Messi often runs at high speeds while controlling the ball. His quick changes in direction show how he uses force to overcome inertia. Each shift in direction requires precise force application, illustrating Newton’s First Law.
Lastly, think about a long pass in soccer. The ball travels a long distance, maintaining its motion due to inertia. The pass continues until it reaches a player or an obstacle. This is another clear example of Newton’s First Law in action.
Credit: www.grc.nasa.gov
Training Techniques And Physics
Training techniques in soccer often use various scientific principles. Physics plays a vital role in understanding and improving player performance. Newton’s First Law of Motion, which states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by an external force, is key.
Incorporating Physics In Training
Coaches use physics to develop better training methods. For example, understanding the force needed to stop a moving soccer ball helps players improve their defensive skills. Training with different ball speeds and angles can mimic game situations. This makes players more prepared during matches.
Another aspect is player movement. Newton’s First Law explains why players need to maintain their speed and direction. Training sessions often include drills that focus on maintaining momentum. This helps players to stay in motion and avoid unnecessary stops. These drills improve their ability to move quickly around the field.
Improving Performance Through Understanding
Understanding physics can also help in injury prevention. Knowing how to distribute force properly when kicking or tackling can reduce the risk of injury. Players learn the best ways to apply force without harming themselves. This knowledge extends their careers and keeps them on the field longer.
Players can also use physics to improve their shots on goal. By understanding the angles and force needed, players can make more accurate shots. Training exercises that focus on these aspects improve scoring chances. Using physics in this way makes players more effective and confident in their abilities.

Credit: www.shutterstock.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Soccer Illustrate Newton’s First Law?
In soccer, a ball remains stationary until kicked. Once in motion, it continues moving until friction or another force stops it.
What Is Newton’s First Law In Soccer?
Newton’s First Law states a soccer ball stays at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force.
How Do Soccer Players Use Newton’s First Law?
Soccer players apply force to the ball to change its motion, demonstrating Newton’s First Law in action.
Why Is Newton’s First Law Important In Soccer?
Understanding Newton’s First Law helps players predict ball movement and control their actions effectively on the field.
Conclusion
Soccer offers a practical view of Newton’s First Law of Motion. Players stop when forces act on them. They change direction when kicked or pushed. The ball rolls until friction slows it down. Understanding this law helps players improve their game.
Coaches can use these principles for better strategies. This connection makes soccer both fun and educational. So, next time you watch a game, think of Newton.


